You’re probably looking for some guidelines on how to write a business plan for an app. Congratulations! You have found the most comprehensive guide on how to write a business plan for a mobile app. Ideation, planning, and execution are all important steps to consider. These are the cornerstones of every project’s success, and they are interconnected. In the rapidly shifting world of information technology, it is hard to predict success with 100% certainty. However, if you devote enough time and effort to each of these cornerstones, your chances of reaching the top will increase significantly.
On the other hand, some business people choose to ignore creating a business plan for a mobile app. These people think that practice is a better way to get the results they want. They hope that spontaneous decisions will help them get to the top of the manufacturers’ list. Unfortunately, this sort of approach never delivers positive results. It’s important to remember that having a plan is the best way to be successful. So, let’s go further into creating a business plan for a mobile app.
What is the importance of having a business plan for a mobile app?
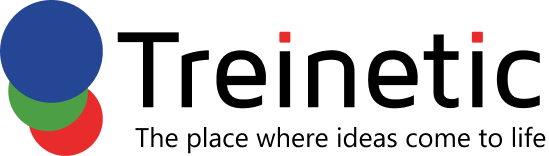
The market for mobile apps is expanding at a rapid pace. Getting into the game before the market gets too crowded is becoming more common.
According to Statista, worldwide mobile app revenues reached more than 365 billion U.S. dollars in 2018. According to projections, paid downloads and in-app advertising are expected to produce more than 935 billion dollars in mobile apps by 2023.
Creating a useful and successful app isn’t as simple as you may assume, despite how attractive it seems. The first step toward a successful launch should be creating a business plan for a mobile app.
A thorough business plan for the smartphone app is a guide for everyone participating in the project. It also tells you how to get the app out into the world in the most profitable way. The process of creating a successful mobile app business plan is rather simple. When you write a business plan, you’ll get a clear picture of your app, as well as information about how to market and finance it.
What are the components of a business plan for a mobile app?
The most important issue to address in a business plan is whether or not the product is profitable to produce. When drafting a business plan for a mobile app, you’ll need to estimate the cost of development and commissioning as well as the timeline for when your project will provide a return on investment.
Creating a reliable and stable mobile application for enterprises, individuals, or non-profit organizations should be your goal in this case. Only then will your app be competitive. Your business plan for a mobile app must have the following:
– Business plan for mobile app: Executive Summary
The executive summary is the first thing we will look at now. This is the first and most crucial section in your business plan for a mobile app since it is the first thing an investor will see and read. There should be no detailed information about how your product works in the executive summary form, so it should be simple and clear. Your executive summary should include information on the current market situation, your target client, and what unique problems your application can address.

Make your proposal unique so that your company stands out from the rest. Put another way, it would be best to create a unique value proposition (UVP.) Put yourself in your investor’s shoes and imagine that your executive summary is the trailer for a movie, with your investor as the audience member. Would they be interested in seeing your movie?
Make a list of your objectives. Base your objectives on your business analysis. Investors will be looking to see if your goals align with their requirements. You’ll also need to figure out your exit strategy’s ultimate aim. To increase your company’s attractiveness, prepare a list of your financial needs and how the funds will be utilized. One of the most critical aspects of developing a startup business plan for your mobile app is ensuring that the process is as transparent as possible at every level.
– Business description
Starting with a description of your company and concluding with a summary of your mobile app idea, this section of your business plan for a mobile app helps introduce your business. This part will show investors what your company stands for and your mission is. It will also show them how you see your product and what you think are the most important factors for your success. Investors need to know this information now more than ever.
– An overview of the company
Here is where you should describe your company, covering the following points:
-
- Type of business structure
-
- Your company’s history
-
- Location of your company
-
- Team/remote team
-
- Problem
-
- Mission
-
- Statement of the concept
Focus on the present situation of your project’s processes, such as the feedback from investors and lenders, in your mission statement. Defining how things are now while focusing on the future and your motivation in the vision statement are key components of the mission statement.
– The company’s history
In this section, you should describe the history of your business, the formation of your team, and how you came up with your idea. It’s also a good idea to talk about the main stages of your company’s growth and the experience that comes before the product goes on the market.
– Your team
Because your app development team is the core of the project, the team section of the company description is often the most significant section describing the company. Names, positions, job experience, and duties within the company should be included for each individual on your list of employees. You may also form a committee to assist you in making critical choices. It would help if you had experts on your committee who have previous industry expertise.
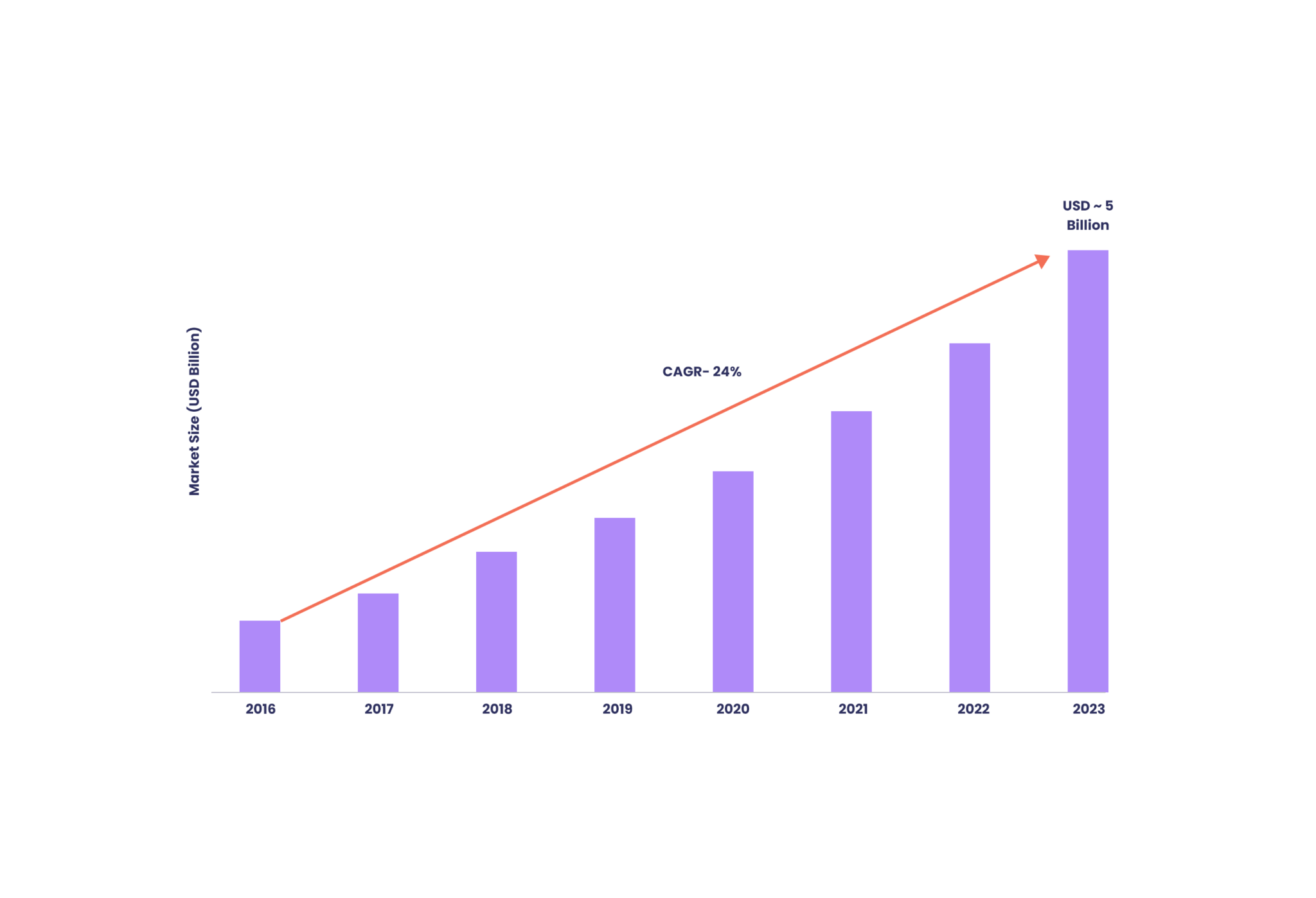
Analysis of the market
When it comes to bringing your app concept to life, information regarding the market’s current status should be your primary consideration. You should know what’s going on in your industry, have the most up-to-date information, and make a short-term strategy. In other words, you should have a market analysis in place. This part of your business plan shows how well your project will work.
– Market forecasts
When writing a business plan for a mobile app, forecasting is essential. Whether it’s for application development or a software startup, any business plan will benefit from forecasts from credible research organizations such as Nielsen, Forrester, etc. Besides that, you can include statistics on the growth of mobile application businesses and the amount of money invested.
A realistic market for your product, a sufficient number of consumers in a market, and, therefore, the willingness of those customers to spend a sufficient amount of money to have their issues solved are your primary objectives in doing market research. Determine whether or not the consumer believes that your unique application fulfills a requirement.
– SWOT analysis
Using a SWOT analysis, which is a kind of strategic planning, you can provide a structured description of your situation and identify opportunities and threats. Using SWOT analysis, you may investigate products, businesses, regions, and even whole countries. SWOT analysis is an acronym that stands for:
-
- Strengths
-
- Weaknesses
-
- Opportunities
-
- Threats
It’s very natural for a company to have flaws, and being aware of possible issues will serve as a powerful drive for finding answers and minimizing any risks your company may be required to take.
Marketing strategy
To get your product into the hands of your consumers, you need a solid marketing strategy in place. This requires convincing investors that you really have such a winning marketing plan. If you want to be successful with your mobile application, you need to use the following marketing strategies:
– Research the target audience
The first stage is to attract your target audience by identifying a specific group of consumers to whom you want to market your product or service. Demography, habits, online behavior, and lifestyle should be used to figure out who this target audience is. Analyze how your ideal client will interact with your app.
– Competition research is important
Competitor research is a critical component of business analysis. This information will assist you in highlighting the characteristics that separate you from your rivals and improve your processes and resolve problems in your marketplace.
– Create a landing page
A landing page for your mobile application can assist you in expanding your target audience as well as informing users about new features and upgrades to the app itself. Include the application’s name, a description of its capabilities, promotional videos, and other pertinent information on your page.
– App rating
If you want your app to show up higher in search results in the app stores, you need to improve it. For example, you can speed up the load time of your mobile app. A high ranking in search results will draw people’s attention to who could become customers.
– Product growth
There are many different approaches to growing their user base when it comes to app startups. In addition, each firm has its own business plan for entering new sectors. It only makes sense to launch a major advertising campaign, for example, in areas where customers are aware of your product or service benefits. Uber and Houseparty are two examples of apps that have done well with big marketing campaigns.
Financials
At long last, the moment has arrived when you can move on to the financial section of your business plan for the mobile app. Before you can go further, you need to know exactly what type of funding you’ll need. Furthermore, a prospective investor should understand the funding requirements when reading this section of your business plan for the mobile app.
Every major forecasted model is included in the financial model, typically a three- to five-year projection of all major forecasted models. These models include profit and loss statements, cash flow statements, balance sheets, start tables, and valuations. If you want to accurately assess the real cost of your assets and distribute them most efficiently, your financial record must have the following components:
– Startup costs or funding required
Communicate with your investors about the expected cost of the project. Because such figures are subject to fluctuation, we recommend setting reasonable estimates and allowing for unexpected costs.
Costs of all kinds:
-
- One-time cost
-
- The costs that occur regularly (regular expenses, for example, rent and insurance)
-
- Costs that are fixed (costs that will remain the same regardless of the state of your business)
-
- Costs that are subject to change (e.g., salaries).
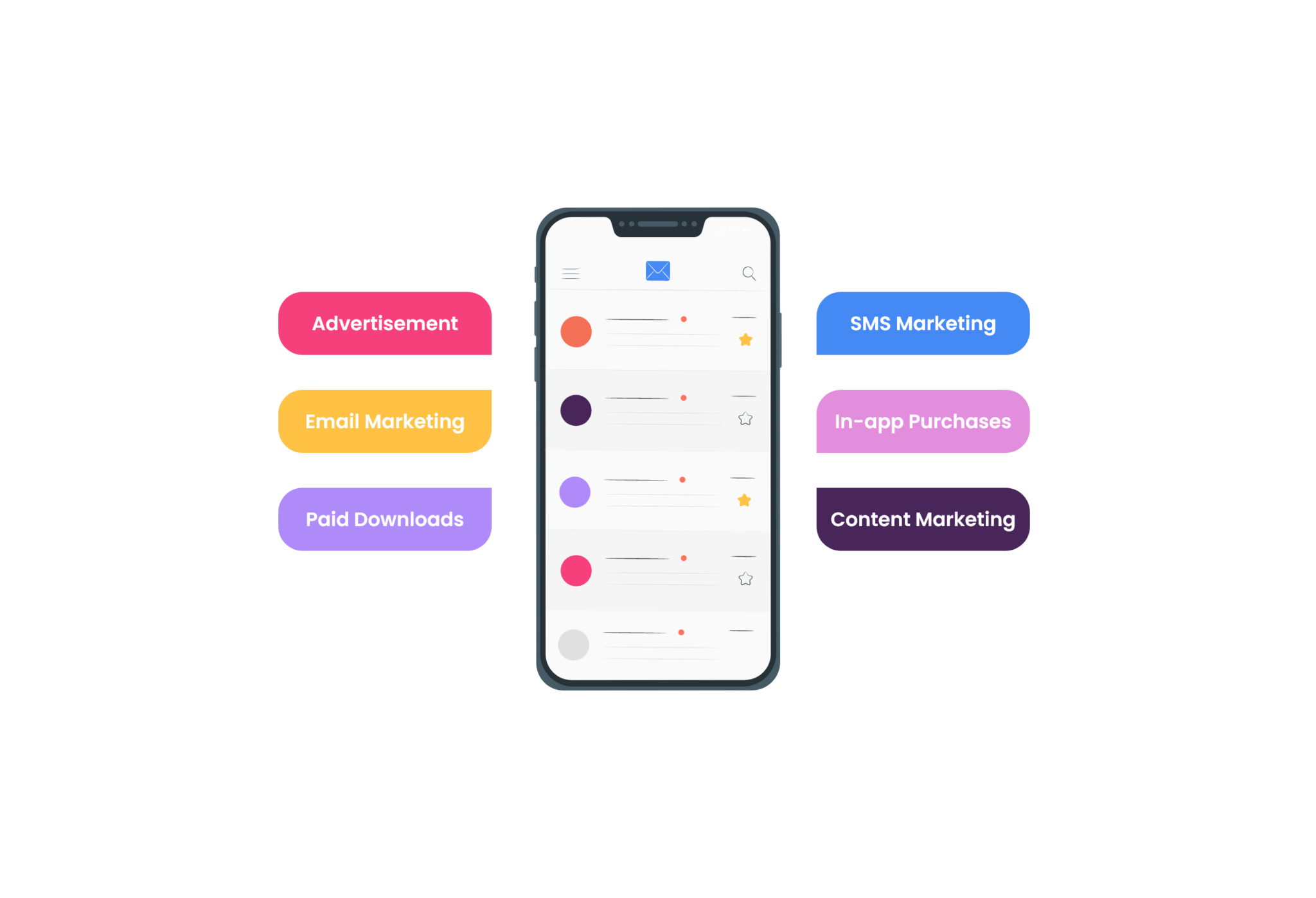
– Developing a monetization strategy
The following are some of the most prevalent methods of monetizing an application:
-
- Advertising
-
- Charging for the application: If your business model calls for a paid application, you must persuade the customer why they should pay and what they will be receiving in exchange for their money.
-
- In-app purchases: This is a common way to make money with iOS and Android apps.
-
- Using subscriptions to generate revenue is a common monetization approach, and it works until the user chooses to cancel the subscription. Most subscription applications provide an onboarding time or a free trial period.
Monetization is a critical component when developing a business plan for mobile apps. To learn more about mobile app monetization, we recommend reading our thorough mobile app monetization guide.
Treinetic’s final thoughts on a business plan for mobile apps
Some people get very excited about ideas but don’t know how to make them real. They learn that mobile apps are profitable, so they learn mobile-related languages and frameworks. Then they try to do something they don’t know how to do. It’s as if they’ve already failed before they’ve even begun.
However, the steps outlined here should help you build a more successful app development plan. The fundamentals are monetization, financial metrics, and determining what makes your product stand out from the competition.